Contents
Pupil- Aperture of The Eye
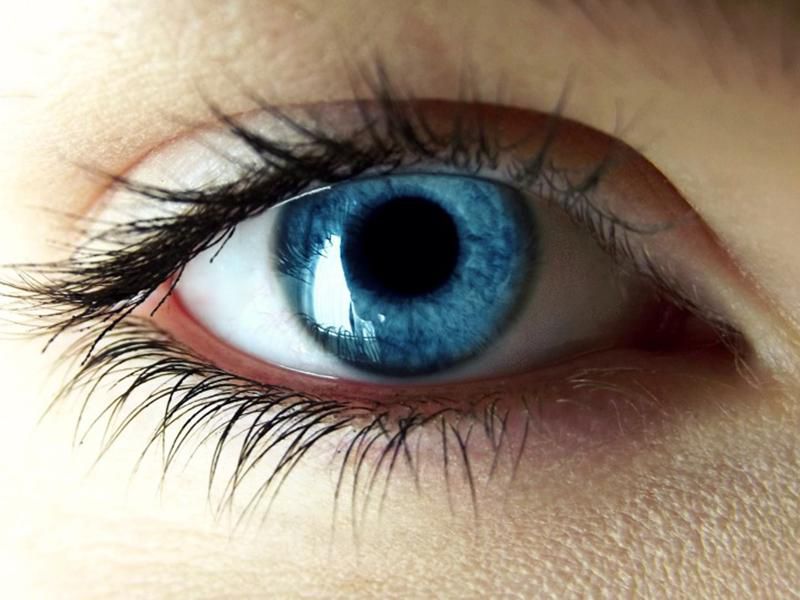
The pupil of the eye is the black circle in the center of the iris. This light is then focused on the retina, which is the layer of light-sensitive cells at the back of the eye. When it is dark, our pupils dilate or open wider to allow more light in.
What Is A Pupil?
It is the center opening of the eye which helps in the entry of light into the eye. The pupil aperture regulates the amount of light entering the eye. The opening in the center of the iris is called a pupil. An iris is a structure inside the eye that provides Gunn’s or to the eye. It helps in allowing the light to enter the eye so that it can fall on the retina so that we can see the object.
The pupil-aperture inside the eye is perfectly round in shape and exactly equal in size. The light which passes through the pupil and falls on the retina gets completely absorbed by the retina so the pupil-aperture is black.
The cataract condition can also be detected if the pupil-aperture is either cloudy or pale in color. This is because the lens is present behind the pupil inside the eye which gets clogged or opaque during a cataract. The normal color of the eye can be restored if the cataract has been treated completely through the help of an intraocular lens which replaces the cloudy or opaque lens.
The pupil-aperture can also change its color i.e., it can appear red Gunn’s rein some photos due to light produced by flashlight while taking a photo. The appearance of red eyes depends on the side of the gaze while taking a photo.
Functions of pupil
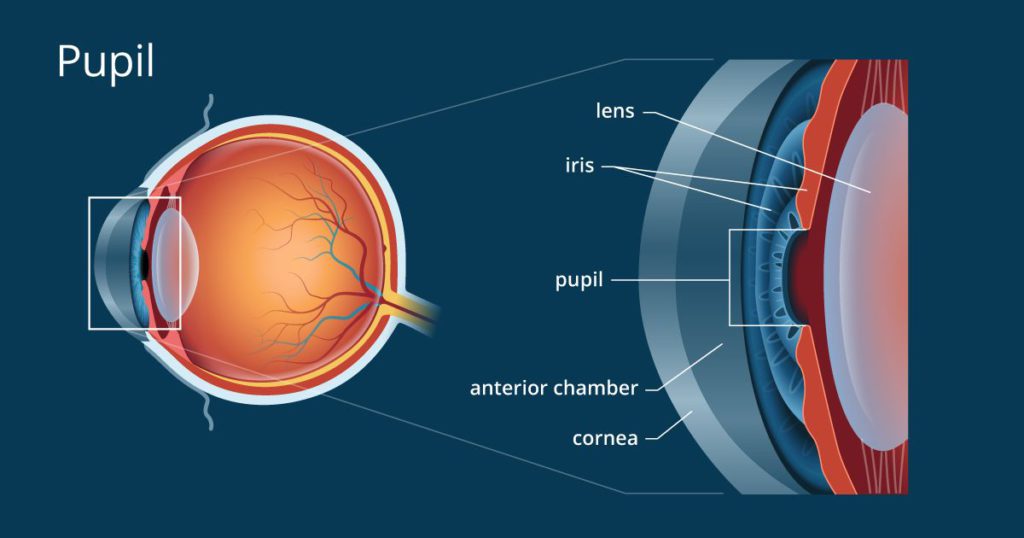
The iris and pupil work in coordination to check the amount of light entering the eye. It acts as the aperture from where the light enters the eye and the iris as the diaphragm which controls the light by changing the size of the aperture.
Its size is maintained by a set of muscles that is present in the iris. To check the size of the aperture, one muscle reduces the size and another one increases the size. This is also called construction and dilation of the pupil-aperture.
The entry of how much light inside the eye through the aperture is controlled by this process of iris muscles. The constriction of the pupil-aperture is required during bright conditions when too light is present. This light can affect the eye by increasing glare inside the eye and can also cause damage to the retina as well as the lens.
The dilation is required when is not much light in the surroundings so that objects can be seen in such conditions also to improve the night vision of the retina. The amount of light entering the eye is restricted by the aperture in the iris, the pupil-aperture. In a dark room, a person’s pupils are large, perhaps 8 mm (0.3 inches) or more in diameter.
When the room is lighted, there is an immediate constriction of the pupils, the light reflex. This is bilateral so that even if only one eye is exposed to the light, both pupils contract to nearly the same extent. After a time, the pupils expand even though the bright light is maintained, but the expansion is not large. The final state is determined by the actual degree of illumination.
Size of The Pupil
The size is different in different people ranging in various age groups. In children, the pupil-aperture size is large and also in young people. In elderly people, the pupil is small in size. The people can also have large as well as small pupils. The pupil size of a normal person is also different in different light conditions such as in bright environments, the size can be about 2 to 4 mm and in dark conditions, the pupil-aperture size can be 6 to 8 mm.
The accommodative pupillary response is a condition that is seen while focusing on a near object, the size of the pupil decreases and constricts its size. Muscles in the colored part of your eye, called the iris, control your pupil-aperture size. Your pupils get bigger or smaller, depending on the amount of light around you. In low light, your pupils open up or dilate, to let in more light.
Conditions That Affect Pupil
Adle’s Syndrome
The pupil-aperture in this case has no responsibility towards the light and shows no reaction towards the light. This affects a single eye, not both eyes. The affected pupil has an increased size than the normal pupil. The cause of this syndrome is still unknown but it is believed to be caused by trauma or ischemic condition (lack of blood). This condition has a slow response to accommodation.
Argyll Robertson Pupil
This condition also shows no response towards the light. This condition usually affects both the eyes and decreases the size of the pupils into really small so that they do not react with the light and show any response.
The cause of this condition is unknown and is seen rarely among people and is believed to have an association with diabetic nephropathy and also with syphilis.
Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD)
This is also known as Marcus Gunn’s pupil. This is caused when there is damage in the posterior region of the optic nerve and any kind of severe retinal disease. This can be diagnosed by performing a swinging flashlight test in which the person suffering from this kind of condition shows less constriction of the pupil-aperture than the normal one when the light is swung from unaffected to affected eye while testing the eye. It affects a single eye in a person. The affected eye appears to dilate in the test.
Trauma
The abnormalities in shape and sizes in the pupil-aperture due to traumatic conditions are seen. The penetrating eye trauma to the iris inside the eye is a common cause of pupil size changes. This condition can also occur as a result of complications in cataract surgery or intraocular surgery. However, in trauma, the light responses and the accommodation to light are normal or nearly normal.
Sexual Arousal
In this case, pupil dilation is seen which is confirmed by recent researches. This can help in the evaluation of sexual orientation in sexuality research. However, our eyes naturally dilate every day to adjust how much light comes in through the lens of the eye and to help us focus. When we have a physiological response, such as fear, surprise, or attraction, this can also make our pupils bigger. The dilation of the pupils is also referred to as mydriasis.
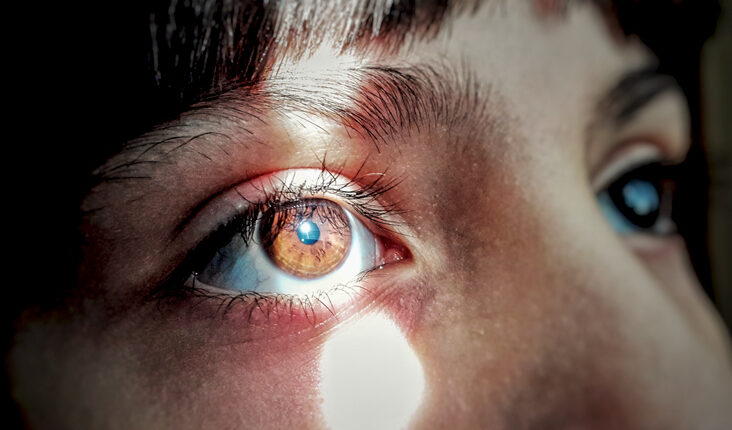
Testing of Pupil-Aperture
The pupil-aperture is tested by the eye doctor with the help of a routine eye examination. In testing, the person is made to sit in a dim-lit room. By placing your gaze on a distant object, the examiner or doctor flashes a small flashlight inside the eye for few times. During this process, the response is observed and noted down.
In-swinging flashlight test i.e. also called Marcus Gunn test. The flashlight is swung from one eye to another eye to see the responses of the pupils in both eyes. The response is normal when the light is directly flashed or indirectly flashed into the eye with the help of a flashlight. The response shown by an eye that has the direct effect of light is called a direct response and the effect of another pupil is called a consensual response.
To test the accommodative response of it, the examiner can turn on some of the lights in the room and allows focusing on a particular object and moves it close to the eye. If it cannot dilate in dim light and does not constrict in bright environments it is considered abnormal i.e., a problem is present in the pupil.
If this condition is not abnormal and shows complete normal functioning and appearance also then it is certified by an acronym which is used for such pupils which are called PERRLA which means pupils are equal, round, and are reactive to light and accommodation.
The pupil is an important structure inside the eye and has a vital role in the eye functioning because it allows the light to enter into the eye. PERRLA is an acronym used to document a common pupillary response test. This test is used to check the appearance and function of your pupils. The information can help your doctor diagnose several conditions, from glaucoma to neurological diseases.
The best way to treat your eyes is to visit your eye care professional and get your eyes checked regularly. He will be able to assess the best method of treatment for your eye ailment.
Visit our website Eyemantra Or mail us at [email protected]. Our other services include Retina Surgery, Specs Removal, Cataract Surgery, and many more.