Contents
- 1 What is Age-related Macular Degeneration?
- 2 Causes of Age-related Macular Degeneration
- 3 Risk factors of Age-related Macular Degeneration
- 4 Types of age-related macular degeneration(AMD)
- 5 Symptoms of Age-related Macular Degeneration
- 6 Diagnosis of Age-Related Macular Degeneration
- 7 Prevention of AMD
- 8 Treatment of AMD
- 9
Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) is a disease in the retina of the eye. This eye disease occurs when a tiny part of the retina called, the macula wears down. It usually happens gradually over time. The macula is a small portion of the retina located on the inside back layer of the eye. AMD cause the loss of central vision while looking at something close or far, the person cannot see details clearly. The patient faces the problem while doing basic daily activities like reading, writing. However, the peripheral vision will stay unaffected. So the person can see things at the sides. For instance, imagine you are looking at a blackboard, you might see what is written at the peripheries of the board but not what is written at the central part. It means you are suffering from AMD.

AMD is a common disease that may get worse over time, therefore it develops in an elder person. It is referred to as Age-related Macular Degeneration. It is the leading cause of severe vision loss in elders above the age of 60. If someone in your family has or had this disease you may be at a higher risk for developing it. Consult with your eye doctor about such risk.
- Age- is the leading factor of severe vision loss in elders above the age of 50.
- Race– People from Asia and the Horn of Africa are at higher risk for developing AMD than other races.
- Gender– may affect the development of macular degeneration. Women tend to develop AMD more than men.
- Hereditary- if you have someone in your family suffering from it then possibly it can be passed on genetically too.
You are more likely to develop this disease if you-
- eat foods high in saturated fat like cheese, butter, and meat.
- are obese, light-skinned, or have a light eye colour.
- are a smoker then could be a major cause of degeneration.
- have high cholesterol levels than having heart disease is another risk factor for AMD
- have hypertension (high blood pressure) the risks increase even further.
This eye disease causes a loss of central vision that occurs in two forms: “dry” (atrophic) and “wet” (exudative). The “Dry” form of macular degeneration is the most common one.

Dry AMD
The “dry” form of macular degeneration is identified by the presence of yellow deposits, called drusen. Few drusen may not cause any changes in vision. However, as they grow in numbers and size, they lead to a dimming or distortion of vision that people usually start noticing when they read.
In the later stages of dry macular degeneration, there is also a thinning of the light-sensitive layer of cells in the macular leading to atrophy or tissue death. Patients may have blind spots in the centre of their eyesight in the atrophic form of macular degeneration. In more advanced stages, patients lose central vision completely.
While there is no specific treatment for dry AMD, studies have shown a potential benefit from vitamin supplements, a Mediterranean diet (Daily consumption of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and healthy fats, Weekly intake of fish, poultry, beans and eggs, Taking dairy products in moderate portions, Limiting the intake of red meat). and quitting smoking.
Wet AMD
The “wet” form of macular degeneration is caused by the growth of abnormal blood vessels from the choroid underneath the macula. This is called Choroidal Neovascularization. These blood vessels leak blood and fluid into the retina, leading to distorted vision that makes straight lines look zigzag and wavy, as well as blind spots and loss of central vision. These abnormal blood vessels and the bleeding from them eventually form a scar, leading to permanent loss of central vision.
As mentioned earlier, most patients have the dry form of the disease and can lose some form of central vision. Still, one must keep in mind, that the dry form of macular degeneration can lead to the wet form.
Although only about 10% of people with macular degeneration develop the wet form, they make up the majority of those who experience serious vision loss from the disease. The less common “wet” form may respond to a treatment including intraocular injections of anti-VEGF medications if detected and treated early.
People with macular degeneration need to get regular Eye Check-ups from the best Eye Doctor in Delhi.
In its early stages, AMD may not have signs and may be unrecognized. Gradually it progresses or affects both eyes. The first symptom of macular degeneration is usually Blurred Vision with a dim, blurry spot in the centre of your eyesight. This spot may get bigger or darker with time.
Symptoms of AMD include:
- Decreased quality/resolution of vision with blurriness and difficulty in reading the fine print, driving, etc.
- Dark, blurry areas in the centre of vision.
- Reduced or altered colour perception.
If you experience any of these symptoms, please consult an Eye Doctor near you as soon as possible.
Diagnosis of Age-Related Macular Degeneration
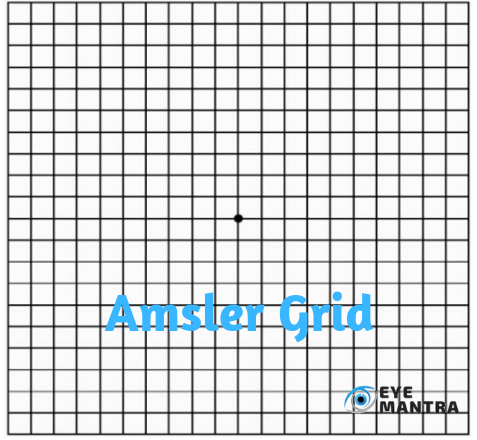
AMD can be detected in a routine eye examination. A good Ophthalmologist would easily be able to detect the presence of drusen. That is tiny yellow deposits under the retina or pigment clumping, during an eye exam. The doctor may ask you to look at an Amsler grid. A pattern of straight lines resembling a checkerboard. If any of the straight lines appear wavy to you, or you notice some of the lines as missing. These can be signs of macular degeneration.
If your doctor detects AMD, you may need an angiography or an Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). In angiography, a dye is injected into an arm vein. Photographs are taken as this dye reaches the eye and flows through the blood vessels of your retina. If any new vessels have developed or vessels are leaking fluid or blood in the macula, the photographs will show their exact location and type. OCT can detect fluid or blood under the retina without the use of a dye.
Early detection of AMD is very important because there are treatments available that can delay or reduce the severity of the disease.
Prevention of AMD
Researchers and doctors believe there is a link between a low nutrition diet and the progression of dry AMD. Making a few changes in diet and lifestyle, and taking Eye Nutrition can slow vision loss. Researchers have linked nutrients such as lutein and zeaxanthin, vitamin C, vitamin E and zinc to reducing the risk of certain eye diseases, including AMD.
- Vitamins. Many studies have shown that for certain individuals, vitamins C, E, beta-carotene, zinc, and copper can decrease the risk of vision loss. Especially, in patients with intermediate to advanced dry AMD. One study was conducted to see if adding other vitamins and minerals to the supplement would improve results. At first, omega-3 fatty acids (fish oil) was added. Next, was a combination of two carotenoids, lutein, and zeaxanthin. These are commonly found in leafy green vegetables and richly coloured fruits and vegetables. The research showed:
- Beta-carotene did not reduce the risk of progression of AMD.
- Adding omega-3 did not reduce the risk of progression of AMD.
- The medicine formula was still found to be protective with less zinc added.
- The test group on a formula with lutein and zeaxanthin and who may not have been taking enough in their diet showed further improvement with the new formula.
- In general, patients who took lutein and zeaxanthin instead of beta-carotene received more benefits.
Treatment of AMD
With “dry” macular degeneration, the macula tissue gradually becomes thin and stops working properly. There is currently no cure for dry AMD, and any loss in central vision cannot be restored. But if detected early, treatments may prevent severe vision loss or slow down the progress of the disease considerably. The options of treatment available are:
Anti-Angiogenesis drugs
These medications ( Aflibercept, Avastin, Eyelet, Lucentis, Macugen) block new blood vessels from developing and prevents leakage from the abnormal vessels within the eye that cause wet macular degeneration. This treatment has brought a major change in the treatment of this disease and many patients have actually regained their lost vision. The treatment may require follow-ups.
To destroy actively growing abnormal blood vessels, High-energy laser light can sometimes be used.
Photodynamic laser therapy
This is a two-step treatment. It involves a light-sensitive drug (Visudyne), which is used to damage abnormal blood vessels. Your Eye Doctor will inject the drug into the bloodstream to be absorbed by the abnormal blood vessels in the eye. He/she will then shine a cold laser into the eye to activate the drug. And damaging the abnormal blood vessels.
Low vision aids
These devices have specialized lenses or electronic systems that help produce enlarged images of nearby objects. They help people whose vision has been lost from AMD. It helps them make the most of their remaining vision.
There are some new treatments underway for macular degeneration. Right now their stages are experimental and have not been used as often since the development of anti-angiogenic medications has developed:
- Sub-macular surgery. Surgery to eliminate abnormal blood vessels or blood.
- Retinal translocation. Abnormal blood vessels are destroyed, which are located right under the centre of the macula. Where a laser beam cannot be placed safely, with surgery. During the surgery, the macular centre is rotated away from the abnormal blood vessels to a healthy area of the retina. It helps to prevent the formation of scar tissue and any further damage to the retina. Once moved away from the abnormal blood vessels, laser treatment is used to remove abnormal blood vessels.
Less common, “wet” AMD happens when fluids leak from newly formed blood vessels under the macula. This leakage blurs central vision. Vision loss can be rapid and severe. If detected early, wet AMD can be treated with intraocular injections of anti-VEGF medications.
People rarely lose complete vision from AMD. They may have a poor central vision, but they are still able to perform most daily activities.
The wet form of macular degeneration is a leading cause of irreparable vision loss. In case both your eyes are affected, you may experience a significant decrease in the quality of your life.
The dry AMD is a much more common form and tends to grow gradually, allowing you to keep most of your vision.
Unfortunately, even after getting treated for wet macular degeneration, the condition can reoccur and requires repeated treatments. Due to this, individuals with AMD must get their vision tested regularly and follow the recommendations of their ophthalmologist. Successful and timely treatment will slow the rate of vision loss and may even improve vision.
If you or your close ones have any of the above-mentioned symptoms. DO NOT DELAY visiting Eyemantra.
Call at +91-9711115191 NOW to book an appointment. Or mail us at [email protected].
Our other services include Glaucoma Surgery, Specs Removal, Computer Vision Syndrome, and many more.
Related Articles:
Best Tips for Eye Care in Pollution
Diabetic Retinopathy: Diabetic Eye Symptoms and treatment in Delhi
Eye pain: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment