Structure of Eye
The eye is considered the photoreceptor organ present in our body. The size of the normal human eye is about 2.5cm in diameter and is spherical in shape. It is located on the orbital part of the skull and has a supply of optic nerve. There are different muscles attached to the eyes which help in the rotation in different directions. The eyes are structurally different but they together perform the function in a coordinated manner in order for us to see.
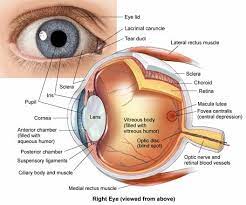
- Eyeball
The eyeball consists of three layers namely, the outer fibrous layer, the middle vascular layer, and the inner layer. The outer layer consists of the sclera, cornea, and conjunctiva. The middle vascular layer consists of the ciliary body, choroid, and iris and the inner layer consists of the retina.
- The outer layer of the eyeball
The sclera is the outermost layer and has a thick membrane of tough fibrous connective tissue. It covers almost every part of the eyeball. It helps in providing attachment of the extrinsic muscle of the eye and maintains the shape of the eye. The cornea is a thin transparent layer present and forms a slight bulge in front. It absorbs oxygen from the atmosphere as well as focuses the light on the retina. Conjunctiva is the outer layer that covers the cornea and provides protection to it. It is made up of a single layer of stratified squamous epithelium.
- The middle layer of the eyeball
The choroid is a thick vascular and pigmented layer which is present below the sclera. The cells absorb light and prevent them from being reflected. It also functions to provide nutrition. The ciliary body consists of two sets of muscles: ciliary muscle and suspensory ligament. The ciliary body is present at the junction between the sclera and cornea. The function of the ciliary body is to attach a lens and hold it in position. It also helps to change the shape of the lens. Iris is a muscular and pigmented diaphragm that hangs in the eyeball in front of the lens. Iris has a small opening called the pupil and the pigment present in the iris gives color to your eyes. Its function is to control the amount of light entering into the eyes by controlling the size of the pupil.
- The inner layer of the eyeball
The retina is the innermost layer. It consists of light-sensitive cells called rods and cones. In the retina, the fovea centralis is the only place that has an absence of rods. Fovea centralis gives an acute and sharp vision. The point where there are no rods and cones present is called a blind spot and is a place where the optic nerve enters the retina.
- Eye lens
The eye lens is a transparent biconvex and fibrous crystalline body that is situated behind the iris. The ciliary muscles control their shape, thickness, and power of accommodation. It helps in the formation of the image on the retina. The eye lens separates the eyeball into two chambers namely the aqueous chamber and vitreous chamber. The aqueous chamber is the fluid-filled chamber that lies between the cornea and lens. The fluid present in the chamber consists of amino acids, glucose, ascorbic acid, hyaluronic acid, and respiratory gases. It helps in providing the necessary nourishment to the lens and cornea. Its function is to refract the light rays to focus on the retina. The vitreous chamber is the fluid-filled chamber between lens and retina. It consists of salts and mucoproteins. It supports the retina and refracts light to focus on the retina for image formation.
How Do Eyes Form Images?
The light reflected from the object helps to see the objects. The light travels into our eyes and then falls onto the retina, the retina then transfers the signals to the brain which then can be seen as the image. The image is formed in our eyes when there is refraction of light entering the eye, focusing of image on the retina by accommodation of lens, the convergence of image, photochemical activity in retina and conversion into the neural impulse, processing in brain and perception of the image.
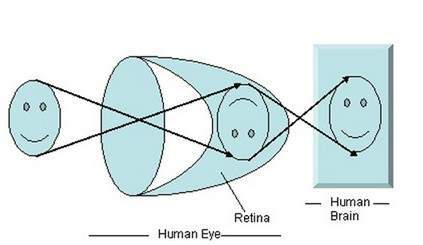
Entering of Light
The light from the object present in the field of vision is reflected and it enters the eye. The light touches the cornea which helps in focusing the light rays. The rays of light are parallel to each other but when they travel from one medium to the other medium then they bend causing refraction. The light needs to reach the retina and passes from the cornea, aqueous humor, lens, and vitreous humor. The light then passes through the lens, it changes its shape according to the distance of the object. In normal eyes, the light is reflected on the surface of the retina. But if you have myopia then the light would be reflected in front of the retina and if you are near-sighted then the light will reflect behind the retina. Such eye defects need corrective lenses so that the image is formed on the retina.
Accommodation of Lens
The accommodation of the lens is the process in which there is a change in the size of the lens so that the light reflected from the object can be made into a perfect focus on the retina. The ciliary muscles help in the contraction and relaxation of the lens according to the distance of the object in the field of the vision. Ciliary muscle contracts if the object is placed near and relaxes if the object is at a distance. The different parts of the eyes have a different refractive index which causes the light ray to bend and reflect on the retina.
Photochemical Activity
The visual information originates in the retina and is detected by the presence of rods and cones. The rods and cones are photo-receptor cells that help information of the vision. The retina also consists of other cells which are connected to each other by the synapse. Bipolar cells, ganglion cells, horizontal cells, and amacrine cells are also involved in image formation. The impulse is directed from the retina to the brain with the help of photoreceptor cells, bipolar cells, and ganglion cells. The nerve fiber carries impulses from both the eyes along the two optic nerves. The optic nerve then transmits the signals to the brain and the image is perceived. Initially, the image formed on the retina is inverted but it is corrected by the brain.
Image Formation of Moving Eyes
The eye has the presence of six different muscles which provide different torques and tension to control the movement of the eye. Rapid eye movement is the eye movement that occurs when you sleep and have vivid dreams. A saccade is the quick and simultaneous movement of the eyes which is controlled by the frontal lobe of the brain. Vestibulo ocular reflex is the movement of the eyes which is opposite to the movement of your head and it keeps the object at the center of vision. Pursuit movement is the tracking movement of the eyes in which the eyes follow the moving object.
Eye Conditions
The functioning of the eye can get affected due to many factors and causes changes in the vision. Some of the common eye diseases which occur among people are mentioned below.
- Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) causes loss of central vision as you get older.
- Amblyopia is also called lazy eye disease and occurs in children in which the children are unable to lift up their eyelids.
- Astigmatism is the eye condition in which the cornea is affected.
- Blepharitis is inflammation that occurs on the eyelids and makes the eyes itchy and irritated.
- Cataract causes clouding in the lens leading to blurred vision. It is an age-related disease.
- A chalazion occurs when there is blockage present on the oil gland and it swells to form a bump.
- Conjunctivitis is an eye infection or inflammation which causes the white part of the eye to turn red. It causes discomfort, pain, and irritation in the eyes.
- Diabetic retinopathy is caused due to high blood sugar levels present in the person suffering from diabetes. It leads to blurred vision.
- Glaucoma is a condition in which the pressure inside the eyes increases which causes blurry vision and can lead to permanent vision loss.
- Retinal detachment can lead to permanent blindness as it is impossible to reverse it.
- A stye is a painful lump formed on the eyelid which can be caused due to infection.
- Uveitis occurs when the iris gets inflamed or infected.
Ways To Keep Eyes Healthy
Healthy Diet
In order to keep your eyes healthy, you should maintain a proper diet as well as stay hydrated. Food rich in omega-3, green leafy vegetables, and fruits should be consumed daily in order to maintain the proper health of your eyes. Vitamin -C is also considered a good source of nutrients to keep your eyes healthy. Keep your blood sugar level in check if you have diabetes.

UV Rays Protection
Protect your eyes from the harmful rays emitted by the sun and the screens. Wear sunglasses when going out. If your work in front of the screen then wears computer eyeglasses to block the harmful blue light being radiated from the screen. This will reduce eye strain and headache.
Blinking
Try to blink more and naturally. Blinking of the eyes creates a tear film in the eyes which clears out the mucus and other particles present in the eyes. Do not stare for a long period of time as it will cause your eyes to dry up.
Hygiene
Avoid touching your eyes with unclean hands. Also never rub your eyes vigorously as it can damage the cornea of your eyes.
Humidifier
Use a humidifier if you live in a hot and dry climatic condition. The hot and dry air tends to evaporate the moisture present in your eyes making them dry and irritated. The use of a humidifier keeps the moisture of the eyes intact and prevents dry conditions.
20-20-20 Rule
Follow the 20-20-20 rule. In this rule, you have to take a break after 20 minutes from your laptop and have to look at an object placed 20m away from you for 20 seconds.
Regular Check-up
Always visit your ophthalmologist for regular check-ups. Visit your doctor if you have changes in your vision or irritation and pain in your eyes is not going away. If an eye disease is detected in the early stages then vision loss can be prevented and proper treatment can be given on time.
The eyes are one of the five sensory organs. They are important as they help us in viewing the environment present around us. You should take good care of your eyes and prevent any infection from occurring in the eyes. A visit to an ophthalmologist is always recommended if you face any eye problem as it may be a symptom of eye disease which needs to be treated at the right time.



