Are you experiencing unusual discomfort or changes in your eyes? It could be more than just a regular irritation. Eye herpes, also known as ocular herpes, is a condition caused by the herpes simplex virus, and it’s more common than you might think. If you’ve been feeling persistent eye redness, pain, or vision disturbances, it’s important to consider the possibility of eye herpes. In this blog, we will explore everything you need to know about eye herpes, starting from its early symptoms to the effective treatment options available.
We’ll help you understand the different types of eye herpes, how they can affect your eyes, and the potential complications if left untreated. So, whether you’re worried about symptoms you’re currently experiencing or want to know about the right treatment early on can make a significant difference in managing this condition, keep reading.
Contents
Eye Herpes (Ocular Herpes)
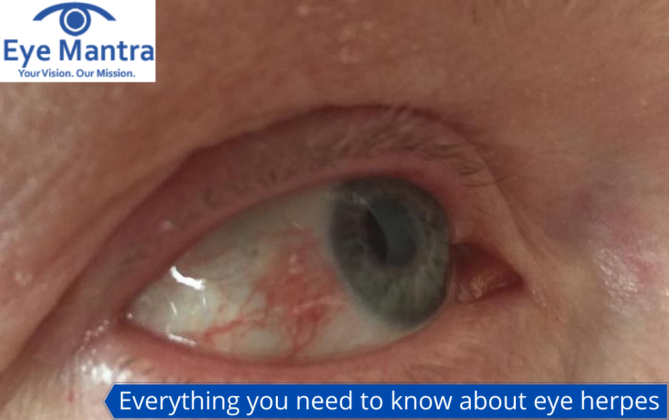
 Eye herpes, medically known as ocular herpes, is an infection of the eye caused primarily by the herpes simplex virus, the same virus responsible for cold sores. This condition can affect various parts of the eye, including the cornea, causing inflammation and irritation.
Eye herpes, medically known as ocular herpes, is an infection of the eye caused primarily by the herpes simplex virus, the same virus responsible for cold sores. This condition can affect various parts of the eye, including the cornea, causing inflammation and irritation.
There are two main types of herpes simplex virus: HSV-1, commonly associated with oral infections (cold sores), and HSV-2, typically linked to genital herpes.
- Most cases of eye herpes are caused by HSV-1, although HSV-2 can also be responsible in some instances.
- The virus can be spread to the eye after contact with an active herpes sore elsewhere on the body or, less commonly, in a dormant state through the nerves.
Eye herpes varies in severity, ranging from mild cases with minimal symptoms to more severe forms that can potentially damage your vision.
It’s important to note that ocular herpes isn’t typically caused by sexual contact; rather, it’s often a result of the virus being reactivated from a previous infection.
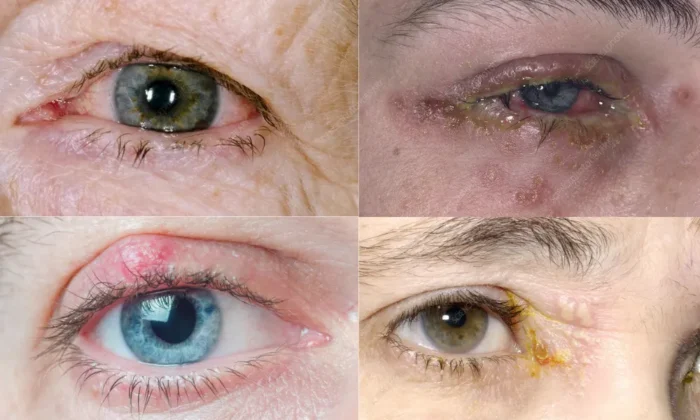
How It Looks Like? Photos
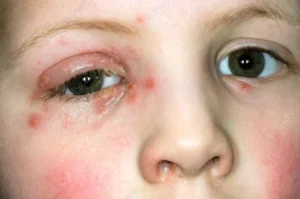
Identifying Early Symptoms of Eye Herpes
Recognizing the early symptoms of eye herpes is crucial for timely treatment and reducing the risk of complications. Here are some of the initial signs you should be aware of:
You may witness inflammation of the cornea, which can lead to irritation or sudden and severe ocular pain. Further, the cornea can become cloudy which further leads to blurred vision. The condition is likely to be herpes if your doctor finds some or all of these symptoms:
- Swelling in the area around the eyes.
- A feeling of something being there in the eye
- Frequent headaches
- Tearing of the eye
- Recurring eye infections
- Sensitivity to light
- Red-eye
- Irritation in and around the eye
- Eyesores
It’s important to remember that these symptoms can also be indicative of other eye conditions. If you experience any of these symptoms, particularly if they persist or worsen, it’s crucial to consult an eye care professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Early detection and treatment are key to managing eye herpes effectively.
Differentiating Between Eye Herpes Types
Eye herpes can manifest in different forms, each affecting the eye in unique ways. Understanding these types is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Here’s a breakdown of the primary types of eye herpes and their respective symptoms:
Type of Eye Herpes | Affected Area | Symptoms and Severity |
Epithelial Keratitis | Corneal Epithelium (outermost layer of the cornea) | Characterized by sores or ulcers on the corneal surface. Symptoms include redness, pain, and tearing, often accompanied by blurred vision and light sensitivity. It’s one of the most common and milder forms of ocular herpes. |
Stromal Keratitis | Corneal Stroma (deeper, supportive layer of the cornea) | This more severe form involves inflammation in the corneal stroma. Symptoms include intense pain, significant vision impairment, deep eye redness, and sensitivity to light. If untreated, it can lead to corneal scarring and permanent vision loss. |
Iridocyclitis | Iris and Ciliary Body | Involves deeper layers of the eye, leading to severe eye pain, blurred vision, redness, and photophobia. Can also cause increased intraocular pressure and potential damage to the iris. |
Trabeculitis | Trabecular Meshwork (drainage area in the eye) | Symptoms may include increased eye pressure, redness, and pain. It can resemble glaucoma and lead to long-term complications if not addressed promptly. |
While epithelial keratitis may respond well to topical antiviral medication, stromal keratitis and deeper infections like iridocyclitis often require more aggressive treatment, including oral antiviral drugs and, in some cases, steroid eye drops under strict medical supervision.
It’s crucial to seek an ophthalmologist’s evaluation for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan, especially if you experience symptoms indicative of the more severe forms of eye herpes.
Diagnosing of Eye Herpes
Diagnosing eye herpes involves a combination of clinical evaluation and specific tests. An accurate diagnosis is vital for effective treatment and preventing potential complications. Here’s an overview of the diagnostic procedures commonly used:
- An ophthalmologist will start with a thorough eye examination.
- They’ll check for signs of infection, inflammation, and any changes in the eye’s appearance, particularly in the cornea.
- Slit-Lamp Examination: This specialized microscope allows the eye doctor to examine the structures at the front of the eye in great detail. It helps in identifying sores, ulcers, or inflammation indicative of eye herpes.
- In some cases, a swab sample from the eye may be taken for laboratory analysis. This test can detect the presence of the herpes simplex virus and confirm the diagnosis.
- A dye such as fluorescein might be used to highlight areas of damage on the cornea. This procedure is particularly useful in diagnosing epithelial keratitis.
- Techniques like optical coherence tomography (OCT) or corneal topography might be used to obtain detailed images of the cornea. This is helpful in assessing the extent of the infection and planning the treatment.
- The doctor may collect a small cell sample known as a culture from the blistered area. This sample then would be sent to a lab for testing for the presence of HSV.
After these diagnostic procedures, your eye doctor will be able to determine the presence and severity of eye herpes and advise on the most appropriate course of treatment.
Is Eye Herpes Curable?
When it comes to eye herpes, a common question many patients have is, “Is it curable?” The straightforward answer is that there is currently no cure for ocular herpes. The herpes simplex virus, once contracted, remains in the body in a dormant state and can be reactivated, leading to recurrent episodes of the infection.
However, while a cure might not be available, the good news is that eye herpes is manageable. With the right treatment approach, the symptoms can be effectively controlled, and the frequency and severity of recurrences can be significantly reduced.
Effective Treatment Options for Eye Herpes
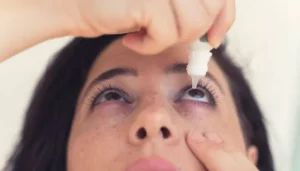 The treatment of eye herpes primarily involves managing the infection and preventing potential complications. Here are the common treatment methods used to tackle this condition:
The treatment of eye herpes primarily involves managing the infection and preventing potential complications. Here are the common treatment methods used to tackle this condition:
- Antiviral Medication:
- Topical Antiviral Eye Drops or Ointments: These are often the first line of treatment, especially for epithelial keratitis. Medications such as trifluridine, ganciclovir, or acyclovir eye drops are used to combat the herpes simplex virus.
- Oral Antiviral Medication: In cases of more severe infection, like stromal keratitis or iridocyclitis, oral antiviral drugs such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir are prescribed. These help control the spread of the virus and reduce the severity of the infection.
- Corticosteroid Eye Drops:
- These may be used alongside antiviral medication, particularly in stromal keratitis, to reduce inflammation and prevent scarring. Their use is carefully monitored due to potential side effects, including increased intraocular pressure and cataract formation.
- Supportive Care:
- Lubricating Eye Drops: To alleviate symptoms like dryness and irritation, lubricating eye drops can be used.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers may be recommended to alleviate discomfort.
- Surgical Interventions:
- In advanced cases leading to significant scarring or vision impairment, surgical options like corneal transplantation may be considered.
- Ongoing Monitoring:
- Regular follow-ups are crucial, as eye herpes can recur. Ophthalmologists might adjust treatments based on the response and any recurrent episodes.
It’s important to follow the treatment plan as prescribed by an eye care professional and attend all follow-up appointments. Early and effective treatment of eye herpes is key to managing symptoms, reducing the risk of recurrences, and maintaining good eye health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, if you suspect you might have eye herpes or are experiencing any eye-related symptoms, it’s important not to wait for them to worsen. Timely diagnosis and treatment are key to managing eye conditions effectively and preventing potential complications.
At the Best Eye Hospital in India, our team of experienced ophthalmologists is equipped to provide you with the highest standard of eye care. Whether it’s for diagnosis, treatment, or just a regular check-up, we’re committed to ensuring your eyes receive the best possible care.
Don’t let eye diseases go unchecked. Take the first step towards protecting your vision and overall eye health. Book your free appointment today or give us a call at 9711116605. We’re here to help you with all your eye care needs, ensuring that your eyes remain healthy and your vision clear.
FAQs
How long can eye herpes last?
The duration of an eye herpes outbreak can vary. An episode of epithelial keratitis, for instance, may last for 1-2 weeks if treated promptly. More severe forms like stromal keratitis can take longer, especially if complications like scarring occur. The virus remains dormant in the body and can reactivate, leading to future outbreaks.
Can you live with eye herpes?
Yes, you can live with eye herpes. While it’s a chronic condition, with proper treatment and management, most people with eye herpes lead normal, healthy lives. Regular check-ups and adhering to prescribed treatment plans are crucial for controlling outbreaks and maintaining eye health.
What foods to avoid if you have herpes?
While there’s no specific diet for herpes, some people find that certain foods can trigger outbreaks. Foods high in arginine, like nuts, seeds, and chocolate, are thought by some to exacerbate herpes symptoms. It’s recommended to maintain a balanced diet, rich in lysine (found in fish, yogurt, and vegetables), which may help counteract arginine.